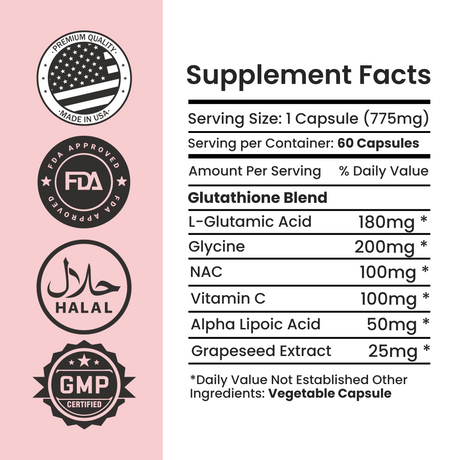
Glutathione, often hailed as the "master antioxidant," is the most abundant tripeptide in the body. It is composed of the amino acids glycine, cysteine, and glutamic acid, and is synthesized mainly in the liver. Glutathione plays a pivotal role in several crucial biological processes, including antioxidant defense, detoxification, and immune function.
Roles of Glutathione
- Antioxidant Defense: Glutathione serves as a linchpin in the body's antioxidant defense system. It combats oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS). These molecules can cause cellular damage, contribute to aging, and are linked to various chronic diseases.
- Detoxification: Glutathione plays a vital role in detoxifying the body. It binds to and facilitates the removal of various toxins, heavy metals, and harmful chemicals. This detoxification process is critical for maintaining overall health and well-being.
- Immune Function: Adequate levels of glutathione are essential for a robust immune system. It supports the proper functioning of immune cells and helps the body defend against infections.
Potential Uses and Effectiveness
While glutathione holds promise in various applications, it is important to note that scientific research supporting its effectiveness is still emerging. Some areas where glutathione may be beneficial include:
- Nerve Damage from Cisplatin: Intravenous administration of glutathione has shown promise in preventing nerve damage and reducing toxicities associated with the chemotherapy drug cisplatin. It is crucial to emphasize that IV products should be administered only by qualified healthcare providers.
- Skin Health: Some individuals use glutathione for its potential skin benefits, claiming that it can lighten skin tone and reduce hyperpigmentation. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is inconclusive, and further research is needed.
- Liver Health: Glutathione is known to support liver health by aiding in detoxification. It is often utilized in clinical settings to treat conditions like alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Side Effects and Precautions
The safety of glutathione largely depends on the method of administration:
- Oral Use: Glutathione is generally considered safe when taken orally in doses of up to 500 mg daily for periods of up to two months. Nevertheless, comprehensive information about potential side effects is limited.
- Inhalation: Inhaling glutathione is also regarded as potentially safe, although information regarding its side effects is scarce.
- Topical Application: The safety of applying glutathione to the skin remains uncertain, with some reports of skin rashes following its use.
Special Considerations
- Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution and avoid glutathione use, as there is insufficient data to confirm its safety in these situations.
- Individuals with asthma are advised against inhaling glutathione, as it may exacerbate certain asthma symptoms.